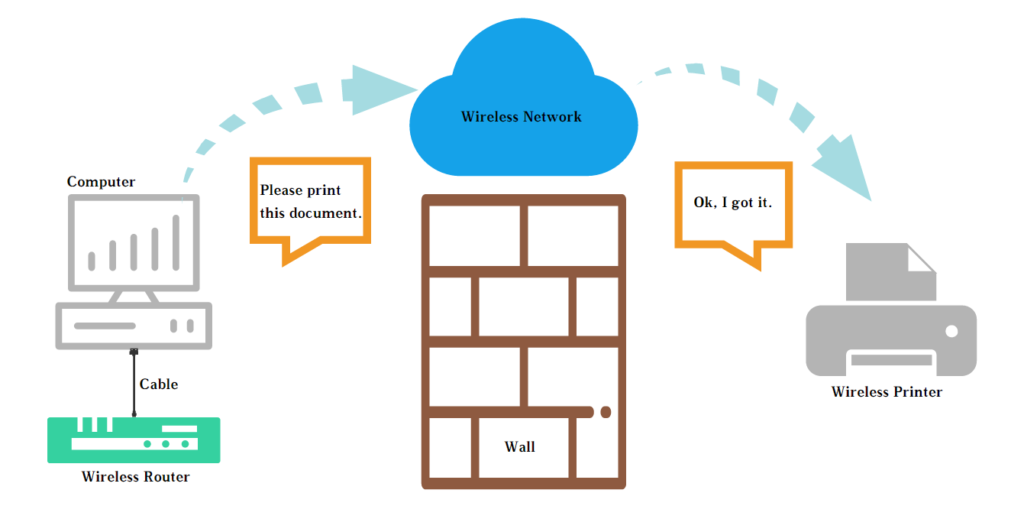
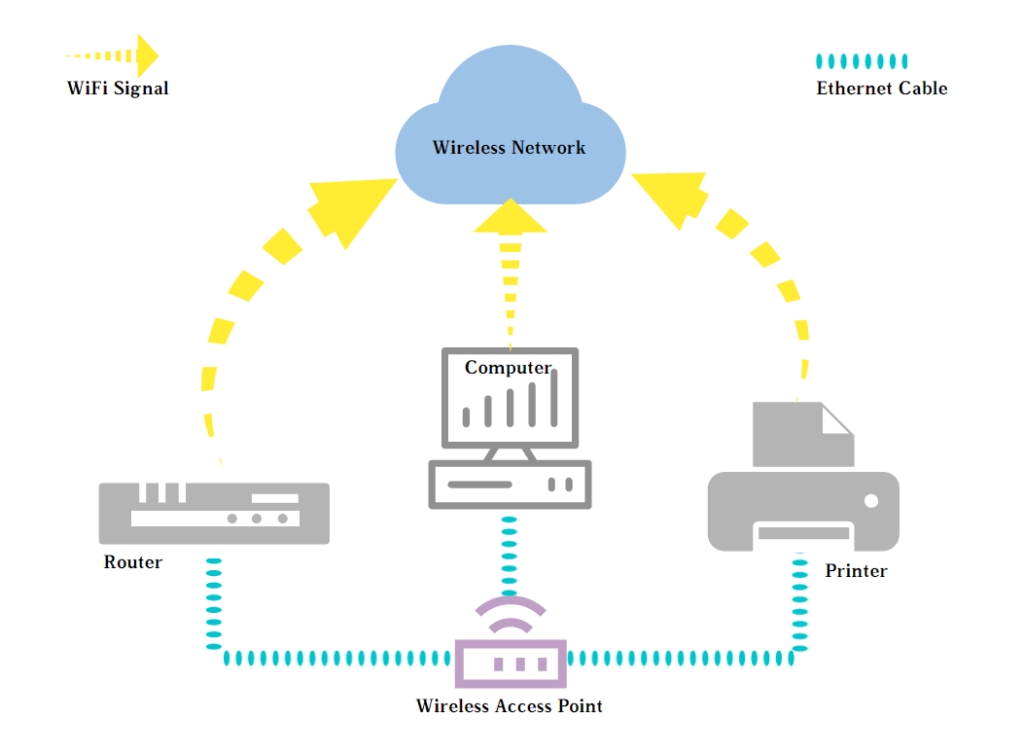
A wireless network access point (WAP or AP) is a hardware device or configured node on a local area network (LAN) that allows wireless capable devices and wired networks to connect through a wireless standard, including Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. A wireless access point acts as a hub of the traditional wired network, and a bridge connecting wired and wireless network. A network access point connects to a wired router, switch, or hub via an Ethernet cable, and projects a Wi-Fi signal to a designated area. Wireless access points may be used to provide network connectivity in office or family environments, covering dozens of meters to hundreds of meters. Most APs use IEEE 802.11 standards.
Types of Network Access Point
Wireless access points can be divided into two types: Simplex AP and Extended AP.
A simplex AP functions as a wireless switch, only transmitting radio signal. When a simplex AP works, it transmits network signal through twisted-pair and converts electrical signal into radio signal after compiling, forming the coverage of Wi-Fi shared Internet access.
An extended AP, commonly known as a wireless router, is mainly applied to Internet access and wireless coverage. Through a wireless router, the share of Internet connection in home Wi-Fi sharing network, as well as wireless shared access of ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Loop) and community broadband can be realised. From security, an network access point is different from a wireless router, in that it does not have firewall functions, and will not protect your local network against threats from the Internet.
Difference Between Network Access Point and Wireless Router
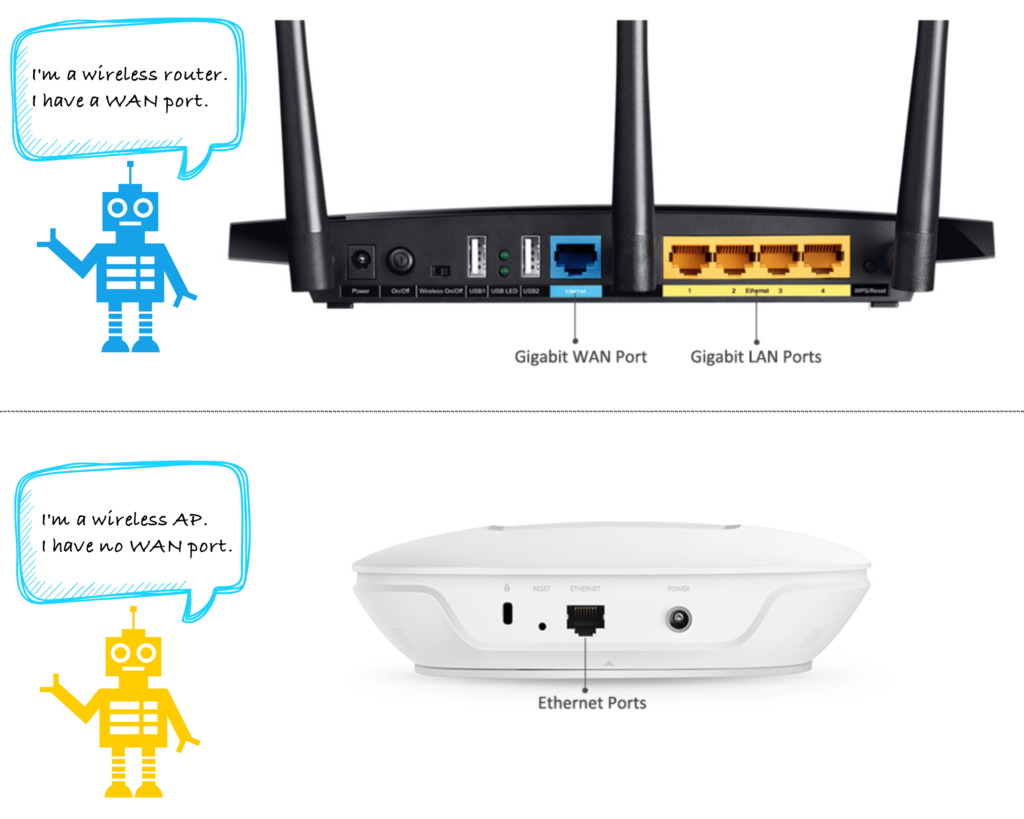
From the appearance, they look almost the same and hard to tell, but they do have subtle differences. A simplex wireless AP usually has a wired RJ45 network port, a power interface, configuration port (USB port or configuration via WEB interface), and fewer indicator lights; while a wireless router has four more cable front-end ports. In addition to a WAN port for connecting higher-up network equipment, four LAN ports can be wired in the internal network, and a router has more indicator lights than AP.
Functions of Network Access Point
AP plays the important role of relay, which amplifies the wireless signal between two wireless points, and enables remote clients to receive stronger wireless signal. For example, if an AP is put in place A, and there is a client in place C which is 120 meters away from place A, it can be seen that the signal from A to C has been weakened a lot. If an AP is put in place B (60 meters between A and C) as a relay, the signal of client in C will be effectively enhanced, and the transmission speed and stability can be ensured.
Another important function of AP is bridging, which is to connect two endpoints and achieve data transmission between two wireless AP. AP is also bridged to connect two wired LANs. For example, there is a wired LAN made up of 15 computers in place A, and wired LAN made up of 25 computers in place B, but the distance between A and B is very far, over 100 meters, and there is no possibility through wired connection, then how to connect the two LANs? AP is needed in both places a and place b to bridge them so that data transmission can be achieved.
The last function is “master-slave mode”, which can achieve one point to multipoint connection. “Master-slave mode” is widely used in the connection between wireless LAN and wired LAN. For example, place A is a wired LAN made up of 20 computers, place B is a wireless LAN made up of 15 computers, and B has a wireless router. If A wants to be connected to B, an AP is needed in A. Initiate the “master-slave mode” and connect AP to the router in A, so that all the computers in A can connect to B.
Summary
Most businesses and homes today rely greatly on the wireless access point (WAP) for data transmission and communication. Wireless access point does make our life more convenient. These devices avoid a mess of wired Ethernet cables like CAT5e, Cat6, etc. Besides, a company, family or school often have to install wired cables through walls and ceilings, while wireless network needs no cables, which contributes great mobility to users.
Related Article: Select Best Ethernet Cable (Cat5/5e/6/6a) for Your Network