The speed and stability of the network is making a great leap forward thanks to the high bandwidth and low attenuation brought by fibre optics. Optical transceiver module is the major building block in fibre optic network, which conveys the information across communication channels for your optical systems. This article offers some rudiments about optical transceiver module and suggestions of choosing fibre patch lead for your transceiver module.
Working Principle of Optical Transceiver Module
An optical transceiver module is a device that uses fibre optical technology to send and receive data. The transceiver module has electronic components to encode or decode data into light pulses and then send them to the other end as electrical signals. To send data as light, it makes use of a light source, which is controlled by the electronic parts, and to receive light pulses, it makes use of a photodiode semiconductor.
Types of Optical Transceiver Module
Optical transceiver module is evolving rapidly to meet the escalating demand for speed and capacity. The tendency is that fibre optic transceiver module is evolving to have smaller size and higher data rate. The common types of optical transceiver module include GBIC, SFP, 10G SFP+, 40G QSFP+, CXP, CFP, CFP2, CFP4, CPAK and QSFP28.
The emergence of GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter) is a milestone of transceiver module development, and it’s of epoch-making significance. As time went on, the size of transceiver was becoming smaller, so SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) transceiver module came into being. It is half the size of GBIC, and it increases the port density of the same line card by two times. But this is not enough to meet the growing need of higher speed network connectivity. So 10G SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) and 40G QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) becomes new market favorites, for they have distinctly higher data rate and the same mini size as SFP. Besides, 100G optical transceiver module is also popular at present, with the types of CXP, CFP, CFP2, CFP4, CPAK and QSFP28. Various types of optical transceiver module can meet all kinds of customer’s requirements.

Optical Transceiver Module Parameters
Optical transceiver module has three main parameters which shows it’s capacity of connectivity. They are wavelength, data rate and cable distance.
Wavelength is the band of light used in the transmission of optical signals. The main wavelength of optical transceiver module is typically around 850, 1300 and 1550 nm, for the attenuation of the fibre is much less at those wavelengths. Besides, multi-mode fibre is designed to operate at 850 nm and 1300 nm, while single-mode fibre is optimised for 1310 nm and 1550 nm.
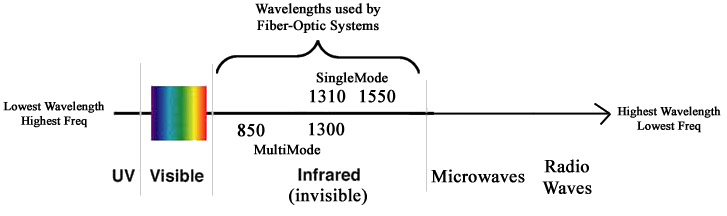
Data rate refers to how many bits of data the optic fibre carries per second. The widely applied data rates are 155Mbps, 1.25Gbps, 2.5Gbps and 10Gbps. The data rate of optical transceiver can provide backwards compatibility. So 155M optical transceiver module is also called FE transceiver, and 1.25G optical transceiver module is called GE transceiver.
Transmission distance is the distance an optical signal can be transmitted directly without amplification. The optical transceiver with the transmission distance shorter than 2km is classified to multi-mode optical transceiver module, while the optical transceiver with the transmission distance over 2km is classified to single-mode optical transceiver.
Except the above three parameters, optical transceiver module has other parameters, which are output power, receiving sensitivity, bias current, extinction ratio, saturated optical power and working temperature.
How to Choose Fibre Patch Lead for Transceiver Module
Optic transceiver modules are correspondingly connected with different fibre patch lead according to the type of their interface. When you choose a fiber patch cable, you need to consider the following factors: fiber type, transmission distance, data rate and transceiver interface.
We suppose that you need to choose a right patch cable used between fibre optic transceiver SFP-10G-SR and X2-10GB-SR. You know that SFP-10G-SR is 10GBASE-SR SFP+ transceiver module for MMF, 850-nm wavelength, LC duplex connector. And X2-10GB-SR is 10GBASE-SR X2 transceiver module for MMF, 850-nm wavelength, SC duplex connector. It’s easy to find that X2-10GB-SR needs SC connector, and SFP-10G-SR requires LC connector. So we should choose patch cable with SC-LC connector with MMF, 850-nm wavelength. In the same way, you can choose the proper fibre patch lead for your transceiver modules.

Conclusion
I believe that you get more familiar with optical transceiver module after knowing its’ types, parameters and how to choose fibre patch lead for it. You also need to know that, the chief advantage of optical technology is its high data transfer rate, which can in practice be several thousand times as fast as a cable modem Internet connection. And fibre optic transceiver plays an important role in fibre optical transmission. For purchasing more high quality optical transceiver modules with low cost or for more products’ information, please contact us at sales@fs.com.








.jpg)
.jpg)