Want to connect all your wired and wireless devices and expand your network with ease? Setting up an Ethernet switch and mesh network may be the best way. Because today it becomes increasingly difficult to use only a router to make your all connections since the approach of IoT. However, Ethernet switch and mesh network will function adequately no matter how many connections you want to make. Here focus on the Ethernet switch and mesh networking.
Why Mesh Networking?
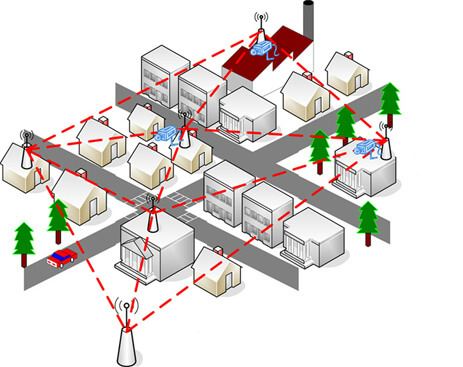
Unlike the stand-alone routers, which will arise signal loss or strength drops when you go away from them, while mesh Wifi networks can use another connection to create a continuous wireless link which minimises the possibility of dead zones. For example, you put your router in the downstairs living room. When you are on the first floor, your phone can connect to the Internet with a strong signal. But when you want to search the Internet in the upstairs office, the signal would degrade. Of course, you can boost a Wifi router’s connection with a signal amplifier. But in that situation, you have to manually connect your phone to the amplifier’s Wifi network. And if you go back to the downstairs, you have to switch back to the main router’s wireless network again. What a pain! Luckily, working with mesh Wifi networks, things are different. In a wireless network, all the nodes are connected with each other which means any node could be an Access Point (AP). Therefore, through the APs, wireless mesh network allows your phone automatically connects to the strongest signal no matter you are in the upstairs or downstairs. That’s better than what we could do with the traditional router Wifi networks.
Figure 1: Mesh network exists in our life.
When to Set Up Ethernet Switch and Mesh Network
If you want to build a wireless mesh network, using an Ethernet switch is a good choice. Before installation, you should consider how much coverage you need in your home. For many people, the money might be better spent on a Wifi router with good quality, since the mesh network equipment like the switches cost too much. But if you want to cover a large area with signal and your home brick is too solid for signal travel through, then use a switch to build wireless mesh network is a way to go.
Use FS Ethernet Switch to Build Mesh Network
Achieving a cheap mesh network is based on switches. FS.COM publishes a set of Gigabit Ethernet switch supporting 1G, 10G, 40G and 100G Ethernet, in order to meet different demands. All the Ethernet switches meet all design and safety standards made by international and industrial organizations like ISO9001, FCC etc.
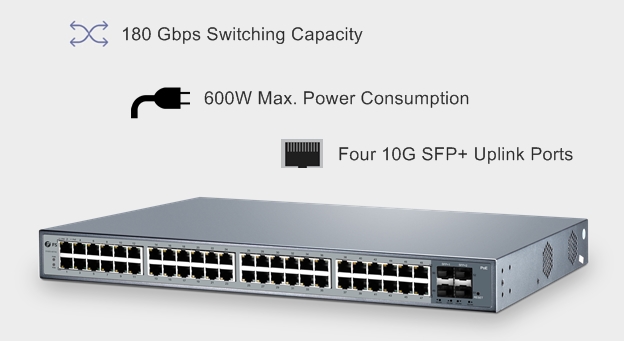
The following is a 10Gb switch named S5800-48F4S. It has 48 1GbE SFP ports and 4 10GbE SFP+ ports. This switch is a Layer2/3 switch with low latency of 2.3us. With the switching capacity, it provides a throughput of 130.95MB. Besides, it supports functions like MLAG, SNMP and so, making it becomes popular on market. Following the S5800-48F4S switch installation guide, you can easily finish the switch installation. Then you can configure the bridge parametres of AP according to the installation instructions to build a mesh network.
Figure 2: S5800-48F4S 48 Port Ethernet Switch
Conclusion
Due to mesh network advantages and disadvantages, we understand why and when to use wireless mesh network. Based on Ethernet switch, mesh networking can spread out fast Wifi across a relatively large area, which makes our life and work more efficiently. So don’t hesitate, pick one Ethernet switch from FS.COM to optimise your Wifi network.