The thriving of 100G network makes the popularization of 100G optical transceiver modules, such as CFP modules, which provide a cost-effective solution for 100G network. What does CFP stand for? How many types of CFP? This article will offer you the CFP wiki.
What Does CFP Stand For?
CFP (C form-factor pluggable) transceiver module’s form factor is specified by the industry standard Multi-Source Agreement (MSA). MSA was designed for optical communication applications and formally launched at OFC/NFOEC 2009 in March. The C stands for the Latin letter C used to express the number 100 (centum), for the standard was firstly developed for 100 Gigabit Ethernet systems. CFP modules are designed to meet the challenge of extreme temperature, humidity and operating conditions. They are suited to 40G and 100G Ethernet data centre applications from the bottom to the top of rack or between racks. CFP was invented after SFP, but is much larger in size to support 100G Ethernet. CFP transceiver modules support both single mode and multimode fibre and a variety of data rates, protocols, and link lengths.
CFP Module Types
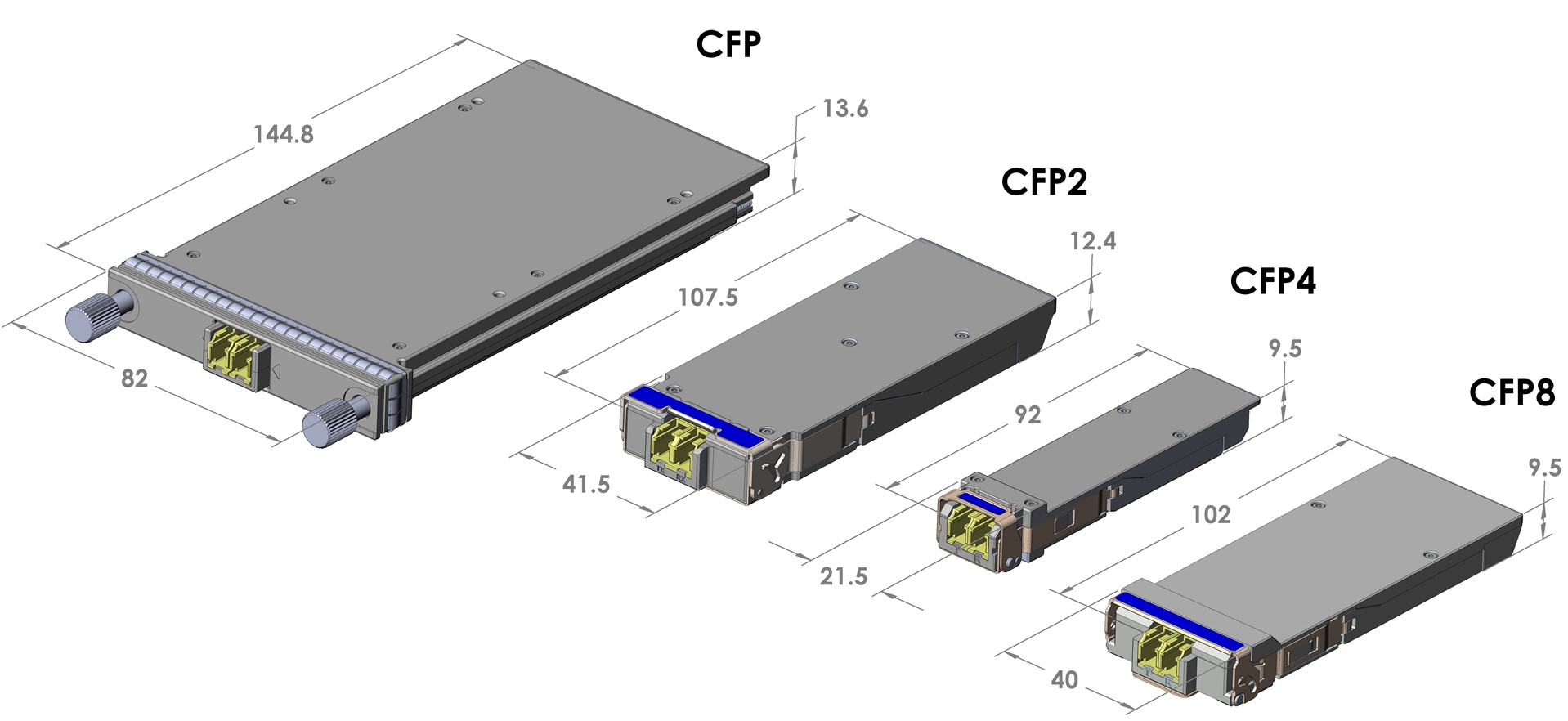
CFP module is regarded as a new ultra high speed pluggable I/O interface. It can support 4x10Gbps, 10x10Gbps and 4x25Gbps variants. There are mainly three types of 40G CFP modules, 40GBASE-SR4 CFP for 150m on OM4 MMF, 40GBASE-LR4 CFP for 10km on SMF and 40GBASE-FR CFP for 2km on SMF. CFP modules provide Ethernet users another option for 40 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity except 40G QSFP+. 100G CFP modules include 100GBASE-SR10 CFP for 100m on MMF, 100GBASE-LR10 CFP and 100GBASE-LR4 CFP for 10km on SMF, 100GBASE-ER10 CFP and 100GBASE-ER4 CFP for 40km on SMF.
CFP MSA defines the CFP2 form factor of an optical transceiver which can support 10Gbit/s, 40Gbit/s, 100Gbit/s and 400Gbit/s interfaces for Ethernet and other applications. CFP2, with half the size of CFP module, can accommodate a wide range of power dissipations and applications. The module electrical interface of CFP2 has been generically specified to allow for supplier-specific customisation around various 4x25Gbit/s interfaces, but it can support 8x25Gbit/s, 10x10Gbit/s, and 8x50Gbit/s.
CFP MSA specifies the CFP4 form factor of an optical transceiver which can support 40Gbit/s and 100Gbit/s interfaces for Ethernet and other applications. CFP4 module electrical interface has been generically specified to allow for supplier-specific customisation around various 4x25Gbit/s and 4x10Gbit/s interfaces. Designed to support SMF and MMF, it is half the size of CFP2 transceiver module.
CFP MSA defines the CFP8 form factor of an optical transceiver to support 400 Gbit/s interfaces for Ethernet, Telecommunication and other applications. CFP8 has the size a little bit smaller than CFP2. Its module electrical interface allows for supplier-specific customisation around various 16x25Gbit/s and 8x50Gbit/s interfaces. Nowadays, 400G is considered to be the next major Ethernet speed for data centres after 100G, thus CFP8 transceiver module has a promising future on the market.
Conclusion
With the above-mentioned info, I believe you get a general idea about what does CFP stand for and the 4 types of CFP modules, including CFP, CFP2, CFP4 and CFP8 and their features. If you need to choose and buy CFP transceiver modules, FS is recommended. FS provides quality CFP modules with different data rates, which are compatible with major brands on the market. FS also provides other transceiver modules. For purchasing more high quality CFP modules with low cost or for more products’ information, please contact us at sales@fs.com.
