With the development of passive optical networking (PON) technology, two PON standards are striking in FTTH solution area and they are Ethernet passive optical networking (EPON) and ATM (asynchronous transfer mode)-based Gigabit passive optical networking (GPON). During these years, it has become a hot topic that which will be more popular in broadband access and optical telecom applications, EPON or GPON? This article will compare these two technologies from the differences of architecture, bandwidth, efficiency, cost, etc.
The biggest difference between the two technologies shows in architecture. EPON employs a single Layers 2 network that uses IP to carry data, voice, and video. While GPON provides three Layer 2 networks: ATM for voice, Ethernet for data, and proprietary encapsulation for voice.
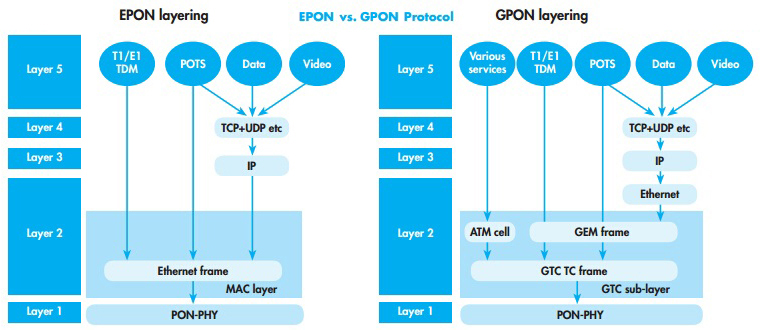
EPON provides seamless connectivity for any type of IP-based or other “packetised” “communications”. Since Ethernet devices are so popular and easy to get, implementation of EPONs can be highly cost-effective.
In GPON, virtual circuits are provisioned for different kinds of services sent from a central office primarily to business end users. This kind of transport provides high-quality service, but includes significant overhead because virtual circuits should be provisioned for each type of service. GPON equipment requires multiple protocol conversions, segmentation and reassembly (SAR), virtual channel (VC) termination and point-to-point protocol (PPP).
EPON delivers symmetrical bandwidth of 1 Gbit/s. EPON’s Gigabit Ethernet service actually constitutes 1 Gbit/s of bandwidth for data and 250 Mbit/s of bandwidth for encoding. GPON promises 1.25-Gbit/s or 2.5-Gbit/s downstream, and upstream bandwidths scalable from 155 Mbit/s to 2.5 Gbit/s. GPON’s 1.25-Gbit service specifies a usable bandwidth of 1.25 Gbit/s, with no requirement for encoding. Gigabit Ethernet interfaces to the aggregation switch, central office, and metro are currently cost-effective to aggregate 1-Gbit ports for transport. But for 1.25 Gbit, there is no way.
Efficiency has to be considered in both directions of a PON. Each PON protocol introduces its own overhead in either direction. In the downstream direction, protocol overhead could be negligible. In the upstream direction, the total scheduling overhead within EPON is from 90.33 percent to 97.08 percent compared to a GbE point-to-point link. In the downstream direction, EPON efficiency reaches from 97.13 percent to 98.92 percent of the efficiency of a point-to-point 1GbE link, while GPON in GTC Encapsulation Method (GEM) mode can achieve ~ 95 percent efficiency of its usable bandwidth. The downstream EPON data rate can be doubled to 2.5Gbps comparable to GPON.
EPON simplifies the networks and needs no complex and expensive ATM and Sonet elements. Thus it helps lower the costs to subscribers. Now the cost of EPON equipment is about 10 percent of the costs of GPON equipment.
Encryption is part of the ITU standard. EPON uses an AES-based mechanism, which is supported by multiple silicon vendors and deployed in the field. And EPON encryption is both downstream and upstream. However, GPON encryption is downstream only.
EPON is an IEEE Ethernet standard and uses Ethernet switches within its silicon, it can natively support all of the 802.1 and 802.3 Ethernet, including VLAN tags, prioritisation, OAM, etc. All Ethernet services can be natively delivered in a manner identical to what is done with switched Ethernet today. As to GPON, it only defines the transport of Ethernet frames. So it has no native Ethernet functionality. Ethernet switches must be placed either in front of or within GPON OLTs and ONTs to provide any additional Ethernet capabilities.
EPON and GPON technologies have been introduced into the market because of service quality and price point. By comparing the differences of the two technologies, it shows EPON is a superior technology for delivering residential and small-to-medium enterprise Ethernet services in terms of its advantages in bandwidth, efficiency, cost, encryption and Ethernet features. So EPON will be employed in FTTH solution area in a large scale earlier and faster than GPON.
Originally published at http://www.streetarticles.com/internet-and-businesses-online/epon-vs-gponwhich-will-be-more-popular
