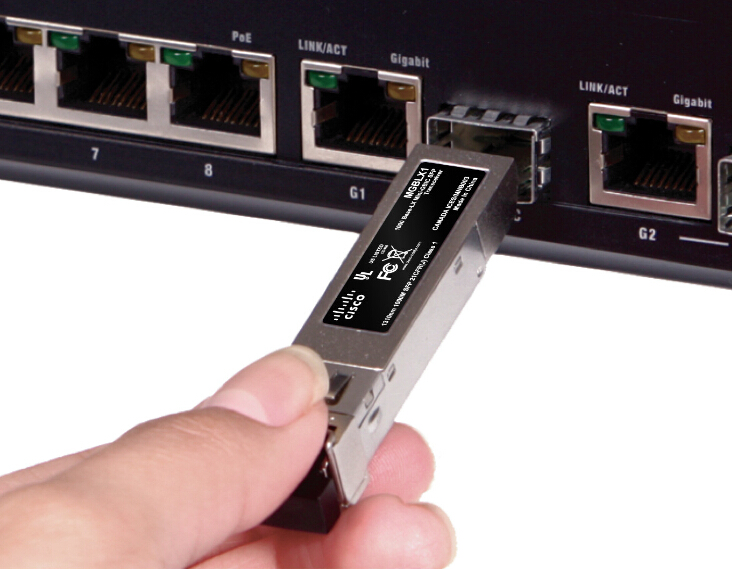
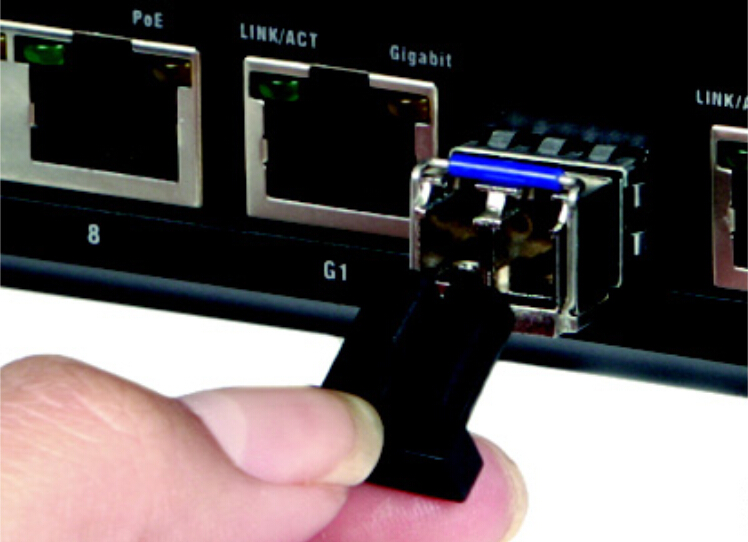
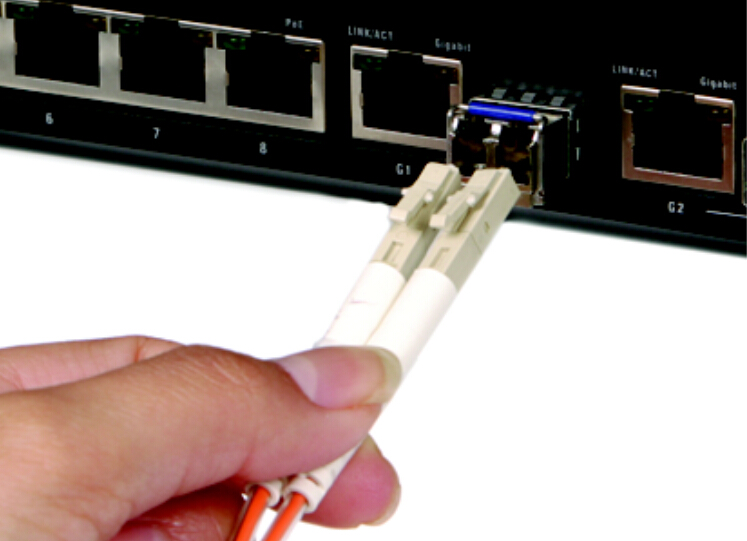
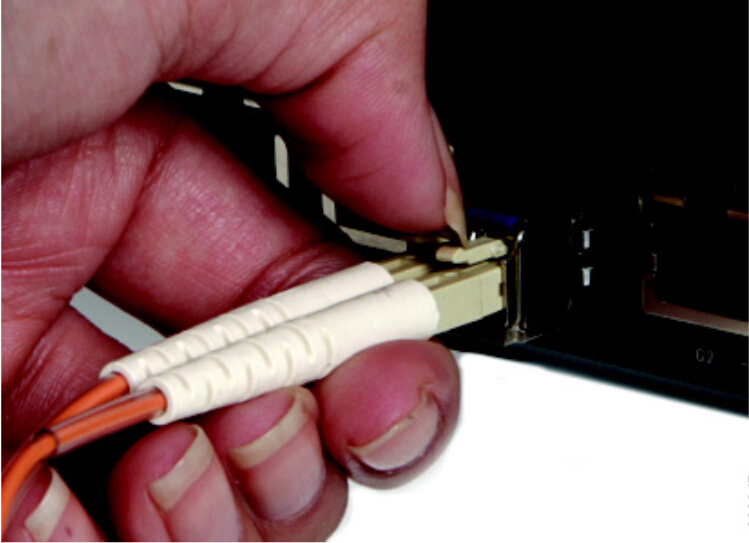
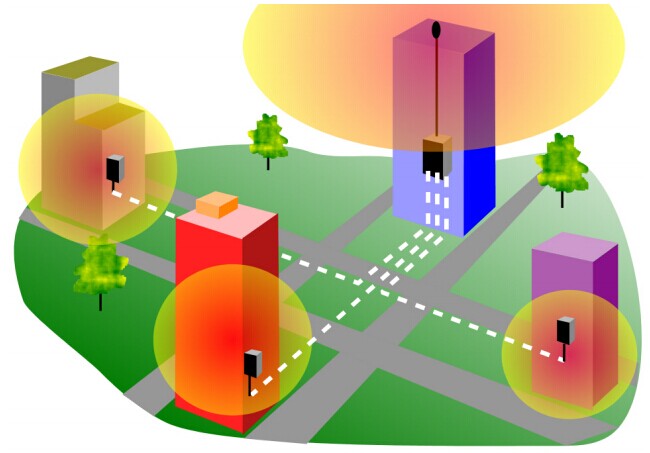
Multi point fibre optic distribution system is the broad wireless technology used to deliver voice, data, Internet, and video services. It has been allocated for that deliever broadband services in a point to point or point to multi point configuration to residential and commercial customers. As a result of the propagating characteristics of signals so that the systems use a cellular like network architecture, though services provided are fixed, not mobile.
In some cases fibre optic distribution system has an ability to connect several remote sites to one base station. One common application is that the repeaters based on a major building and others building such as RF shielding areas and basement which all located in a few miles repeater building. A and the repeater use the head end. A multiple fibre optic transceiver assembly at the base station is commonly called a “head end” The distance end of the fibre is called “remote hub” equipment.
We need to pay attention to that each fibre optic receiver output at the repeater site has individual pads to reduce the composite noise floor. For example, if used the 40dB, an additional 80 dB of combiner port-to-port isolation occurs. In real application, it is a good idea, including regard the taps at test point to read the RF levels. Just used for testing and protection. A similar system that when we used the WDM, if the numbers of fibres are reduced by 50% but a WDM must be added at each remote site and another WDM for each fibre added at the repeater site. In the 4 remote site example, it would be taking 8 WDM’s to operate all the fibres full duplex and 4 fibre optic transmitters would have to be 1550nm models. Then there also a point we need to be careful. Fibre optic transceiver is not frequency selective and the same unit can receive 1330 or 1550nm optical signals equally well. We also measured the noise performance and we are happy to inform you that in line with theory, optic splitters practically do not add any noise. No matter what output we tested, this means that your receiver connected to such network would also show very high quality readings.
When we use the fibre optic links in the fibre optic distribution system, sometimes we need fibre optical splitter to split the signal which carried. The system designer has the choice of splitting either the optical or RF domain. The function of optical splitter is familiar to RF splitter. Other parts of the incoming fibre optic network are connected to the transmission of output, and the terminal device is connected and the another main part is its direct part. There are also splitters that divided the input into 2, 4 or more outputs. According to the structure and locations of fibre optic splitter, in the fibre optic network, we need different split ratios of splitter, such as 1×2, 1×4 and 1×8 splitter?and so on. Moreover unused single mode fibre cable, specific products can see at 50m single mode, it also can strengthen the signal used for the RF over fibre optic systems between the connected buildings for data communication and spare fibres.
Article Source: http://www.fiber-optical-networking.com/2015/02/09/fiber-optics-based-on-multi-point-fiber-distribution-systems/