In the modern interconnected era, robust and effective network communication is crucial for the success of businesses. To ensure seamless connectivity, it is vital to grasp the underlying technologies involved. Among these technologies, SFP and QSFP ports on switches play a significant role. This article aims to simplify these concepts by providing clear definitions and highlighting the advantages and applications of SFP and QSFP ports on switches.
What are SFP and QSFP Ports?
SFP and QSFP ports are standardized interfaces used in network switches and other networking devices.
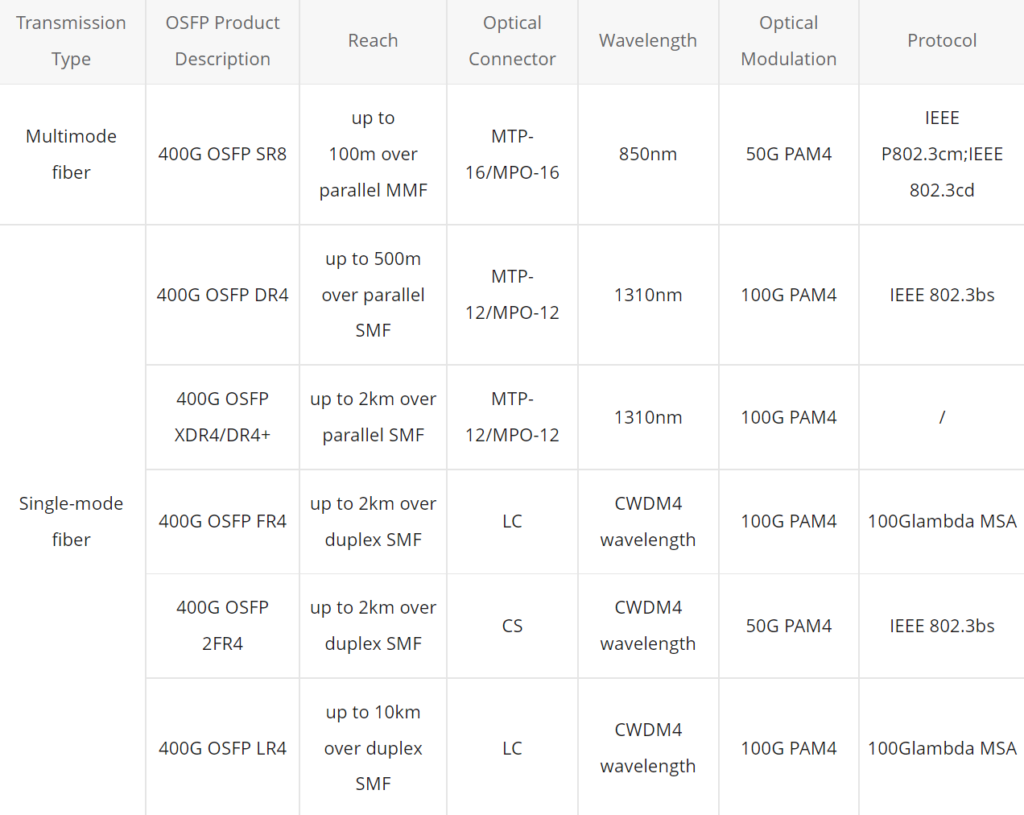
SFP ports are small in size and support a single transceiver module. They are commonly used for transmitting data at speeds of 1Gbps or 10Gbps. SFP ports are versatile and can support both copper and fiber optic connections. They are widely used for short to medium-range transmissions, typically within a few hundred meters. SFP ports offer flexibility as the transceiver modules can be easily replaced or upgraded without changing the entire switch.
QSFP ports are larger than SFP ports and can accommodate multiple transceiver modules. They are designed for higher data transmission rates, ranging from 40Gbps to 400Gbps. QSFP ports primarily support fiber optic connections, including single-mode and multimode fibers. They are commonly used for high-bandwidth applications and long-distance transmissions, ranging from a few meters to several kilometers. QSFP ports provide dense connectivity options, allowing for efficient utilization of network resources.
Differences between SFP and QSFP Ports
- Physical Features and Specifications: SFP ports are smaller and support a single transceiver, while QSFP ports are larger and can accommodate multiple transceivers.
- Data Transmission Rates: QSFP ports offer higher data transmission rates, such as 40Gbps or 100Gbps, compared to SFP ports, which typically support lower rates like 1Gbps or 10Gbps.
- Connection Distances: QSFP ports can transmit data over longer distances, ranging from a few meters to several kilometers, while SFP ports are suitable for shorter distances within a few hundred meters.
- Supported Fiber Types: QSFP ports can handle a wider range of fiber types, including single-mode and multimode fibers, whereas SFP ports are typically compatible with both fiber and copper cables.
Advantages and Applications of SFP and QSFP Ports
- Advantages of SFP Ports:
- Flexibility: SFP ports allow for easy customization and scalability of network configurations.
- Interchangeability: SFP modules can be hot-swapped, enabling quick upgrades or replacements.
- Versatility: SFP ports support various transceiver types, including copper and fiber optics.
- Cost-effectiveness: SFP ports offer selective deployment, reducing costs for lower-bandwidth connections.
- Energy Efficiency: SFP ports consume less power, resulting in energy savings.
- Applications of SFP Ports:
- Enterprise Networks: SFP ports connect switches, routers, and servers in flexible network expansions.
- Data Centers: SFP ports enable high-speed connectivity for efficient data transmission.
- Telecommunications: SFP ports are used in telecommunications networks for various applications.
- Advantages of QSFP Ports:
- High Data Rates: QSFP ports support higher data transmission rates, ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications.
- Dense Connectivity: QSFP ports provide multiple channels, allowing for efficient utilization of network resources.
- Long-Distance Transmission: QSFP ports support long-range transmissions, spanning from meters to kilometers.
- Fiber Compatibility: QSFP ports are primarily used for fiber optic connections, supporting single-mode and multimode fibers.
- Applications of QSFP Ports:
- Data Centers: QSFP ports are essential for cloud computing, high-performance computing, and storage area networks.
- High-Bandwidth Applications: QSFP ports are suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications requiring fast data transfer.
- Long-Distance Connectivity: QSFP ports facilitate communication over extended distances in network infrastructures.
FS Ethernet Switch with SFP Ports: S5810-48FS
Reliable data transmission is essential for enterprises to thrive. In the previous article, we highlighted the benefits of SFP and QSFP ports in achieving high-speed data transmission. Now, we introduce the FS S5810-48FS, a gigabit Ethernet L3 switch recommended as a network solution. It serves as an aggregation switch for large-scale campus networks and a core switch for small to medium-sized enterprise networks, ensuring stable connectivity and efficient data transfer.
- SFP Port Capability: The S5810-48FS is equipped with multiple SFP ports, providing flexibility for fiber optic connections. These ports allow for easy integration and expansion of network infrastructure while supporting various SFP transceivers.
- Enhanced Performance: The S5810-48FS offers advanced Layer 2 and Layer 3 features, ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission. It has a high switching capacity, enabling smooth traffic flow in demanding network scenarios.
- Easy Management: The switch supports various management options, including CLI (Command-Line Interface) and web-based management interfaces, making it user-friendly and easy to configure and monitor.
- Security Features: The S5810-48FS incorporates enhanced security mechanisms, including Access Control Lists (ACLs), port security, and DHCP snooping, to protect the network from unauthorized access and potential threats.
- Versatile Applications: The S5810-48FS is suitable for various applications requiring high-performance networking, such as enterprise networks, data centers, and telecommunications environments. With its SFP ports, it provides the flexibility to connect different network devices and accommodate diverse connectivity needs.

Conclusion
SFP and QSFP ports are crucial for reliable network communication. SFP ports provide flexibility and versatility, while QSFP ports offer high data rates and long-distance transmission. The FS S5810-48FS Ethernet switch with SFP ports serves as an effective solution for large-scale networks and small to medium-sized enterprises. By utilizing these technologies, businesses can achieve seamless connectivity and efficient data transmission. If you want to learn more, please visit FS.com.
Related Articles: